Every one of us is always terrified to see our electric bill. Sadly though, we have no other choice but to accept this reality because electricity is already part of our modern-day existence. The best we could do to minimize our electricity consumption and help in energy conservation is avoidance and or limit the usage time.
Anyhow, there are those household appliances that must be connected and should remain functioning all the time. These types of appliances we can’t do anything if we want them and should be willing to pay the price… that is, your monthly electric bill.
In this article, I will walk you through the things you possibly need to know about home appliance power consumption.
This is to give you an idea of how the power consumption of household appliances is controlled to keep them in check from their source.
Let’s find out….
Understanding Power Consumption
Talking about power consumption is tricky and not easy because of how broad this subject matter is… whereas, if not careful in giving an opinion could result in a lot of confusion because there are much different information based on products distinct application.
But before we go further… let us first find out what is the meaning of power consumption and why it is important to understand.
What is power consumption meaning?
- Power consumption is the electricity or energy used during the operation of electronic and electrical household and office equipment. Or in other terms, it is the amount of electrical energy used per unit time.
- Power consumption can be also the passive electricity consumed or wasted while the electrical appliance is NOT in operation (i.e. OFF/STANDBY mode power consumption)
- Measurement Unit – Watts (W) and or kilowatts (kW)
- Can be measured using a Power Meter
What is a typical power consumption?
According to U.S. Energy Information Administration, electricity consumption in the United States in 2020 was estimated to be about 3.8 trillion kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Where heating (14.2%) and cooling (15.7%) comprise the largest electricity usage in a Residential area.

While computer and office equipment cover the largest electricity usage in Commercial sector.
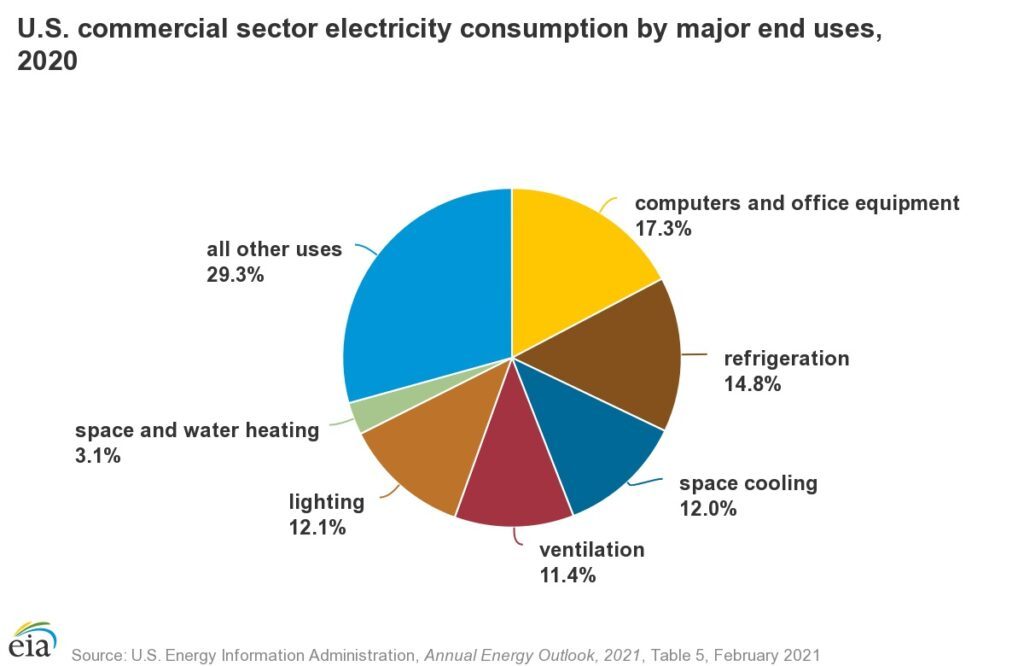
And machines are the largest to consume electricity in the Manufacturing sector.
https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/electricity/use-of-electricity.php
Why is power consumption important?
Addressing power consumption is especially important for all electronic and electrical household and office equipment according to each country of destination.
This is especially true for products that are intended to be sold in Europe.
EU’s Eco-design Directive regulates all electronic and electrical household and office equipment must be in compliance before it can be marketed in Europe.
- All manufacturers and importers are required that all products covered under Energy-related Products (ErP) Directive 2009/125/EC (formerly known as EuP) must comply before they can be sold in any EU country. The ErP directive intends to encourage manufacturers and importers to supply end-users with products that are energy efficient.
- EU’s Energy-Related Products Directive (ErP Directive 2009/125/EC) is an Eco-design Directive and the EU’s way of regulating products to be more energy efficient. It applies to most products that consume energy throughout their lifecycle (e.g., all Major Domestic Appliance and Small Domestic Appliance, etc)
- Electric household appliances in compliance with EU’s Eco-design Directive shall then bear the CE mark and can be marketed in any EU countries
Which Appliances Use the Most Electricity?
The household appliance that consumes more electricity are those major appliances with higher power or wattage and is used for a longer time, such as:
Refrigerators / Freezers / Minibars / Wine Coolers
- These appliances may have lower power but the fact that it has to be constantly ON makes them on top of the list.
- For refrigerators, there are newer designs that employ “inverter technology“ that makes it more energy efficient but the price will be much higher than the normal one.
Air Conditioning Unit (ACU)
- A typical Air-conditioner’s power will be around 3000W. During summer how many hours are you going to open it? 12 hours? 24 hours?
- There are newer designs that employ “inverter technology“ that makes it more energy efficient but the price will be much higher than the normal one.
Washing Machines and Dryers
- A 7kg washing machine will have power of about 2000W. A standard wash time is around 1hour. How many times do you wash clothes per week?
- There are newer designs that employ “inverter technology“ that makes washing machine and dryers more energy efficient.
Dishwasher
- A 12 to 14 place settings dishwasher will have power around 2000W.
- If you use an Extensive washing program that will last for more than an hour will also add up to your electricity consumption and electric bill
Oven
- An oven when used for baking will consume more electricity as it will be working at maximum power (all heaters, fans are working)
- If the oven’s maximum power is 3000W and you bake for 1 hour that adds up and how many times do you use the oven will impact your electricity consumption and electric bill
Electric Water Heater
- Typical electric water heater will have power of about 1500W
- During the winter season you have no other choice but to use it. How long do you take a bath and how many times will impact your electricity consumption and your electric bill
Electric Heater
- A typical freestanding electric heater will have at least a power of about 1500W
- During the winter season you have no other choice but to use it. How long are you going to use it? 24/7? Thus, it will greatly impact your electricity consumption and your electric bill
Dry Iron / Steam Iron
- A typical steam iron will have a power of around 2000W… if you do ironing on weekly basis that means you have clothes that need to be ironed that will be good for 5 days
- How many person’s clothes have to be ironed will dictate how many hours of ironing will be needed and that will also sum up to your electricity consumption and electric bill
How do you Calculate Power Consumption?
As defined above, power consumption is the amount of electrical energy used per unit time.
To calculate power consumption, multiply the power (wattage) by the number of hours the appliance is being used or in operation (time).
- Find the daily power consumption using below formula:
- (Wattage × Hours Used Per Day) ÷ 1000 = Daily Kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption
- Find the annual power consumption using below formula:
- Daily kWh consumption × number of days used per year = annual energy consumption
Or you can make use of the available power consumption calculator (there are many in the web, just search for it)
The result may not be accurate for those appliances that have thermal cut-off. Because after reaching the cut-off temperature, the power will decrease to minimum for several seconds before it re-activates to its maximum power and it will be repeated cycle.
Do you SAVE Electricity by Unplugging Appliances?
As we have defined power consumption above, it could also mean the passive electricity consumed or wasted while the electrical appliance is NOT in operation (i.e. OFF/STANDBY mode power consumption)
Based on my experience doing inspection of all kinds of household appliances for Europe, when verifying OFF and or STANDBY power consumption there will always be readouts.
Seldom will I encounter an appliance with 0W power consumption, see below example.
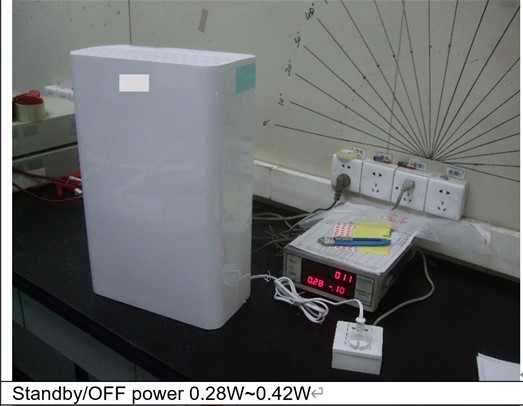

Why the need to verify power consumption at factory sites?
- Because as I have mentioned earlier, all household appliances that are marketed in the EU must comply with EU’s Eco-Design Directive.
- And the Energy-related Products (ErP) Directive 2009/125/EC (formerly known as EuP) covers this requirement about OFF and STANDBY power consumption.
Below are the ErP standard for OFF / STANDBY power consumption:
One year after this regulation has come into force:
- OFF mode should not exceed 1.00W
- STANDBY mode should not exceed 1.00W; or 2.00W if providing information or status display
Four years after this regulation has come into force:
- OFF mode not to exceed 0.50W
- Standby Mode not to exceed 0.50W; or 1.00W if providing information or status display
With the above information…
Thus, unplugging appliances can save electricity because even the product is powered OFF or in STANDBY mode there is energy wasted.
Therefore, make it a habit to unplug any appliances that are not in use, especially for a longer period of time to conserve energy.
Conclusion
To conclude, we’re able to define and understand what is Home Appliance Power Consumption.
Power consumption is not only about the needed power to operate the appliance, but power consumption could also be the wasted energy while the electric appliance is at OFF or STANDBY mode.
We’ve also identified several household appliances that use the most electricity according to the estimated power as well as the estimated usage time.
So, there you have it folks, thank you for reading. If you find this article helpful or if you have questions and suggestions please leave them in the comment area. And I will be glad to answer them as soon as I can.
